Introduction
Welding is one of the most essential techniques used in manufacturing, construction, and repair industries. It allows us to join metal parts together permanently, making it crucial for everything from building bridges and skyscrapers to assembling cars and aircraft. Despite its widespread use, many beginners find welding intimidating due to the technical knowledge and equipment involved.
In this guide, we’ll break down what welding is, the different types of welding, essential tools, and safety tips. Whether you’re looking to start a career in welding or simply want to learn it as a hobby, this guide will help you get started
What is Welding?
Welding is a process of joining two or more pieces of metal (or plastic) by melting the base materials and adding a filler metal to create a strong bond. This is typically done using high heat, but some welding methods also use pressure or chemical reactions.
Unlike bolting or riveting, welding creates a permanent and often stronger connection between materials. It is widely used in industries such as:
- Construction – bridges, buildings, pipelines
- Automotive & Aerospace – vehicle frames, airplane fuselages
- Manufacturing – machinery, industrial tools
- DIY & Hobby Projects – furniture, metal art, home repairs
Types of Welding
There are several types of welding, each with its own advantages and applications.
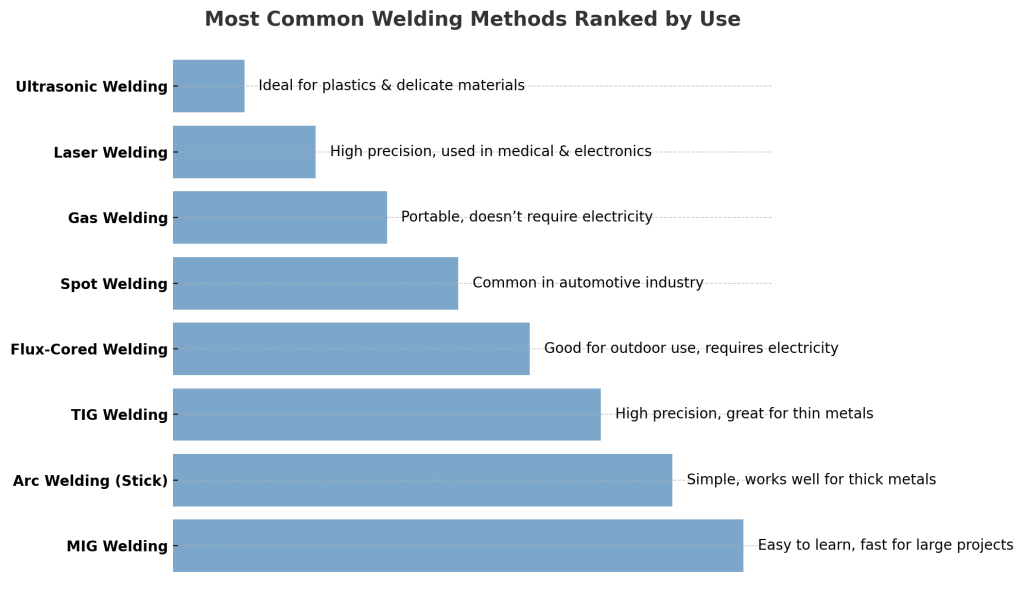
Arc Welding (Stick Welding – MMA)
Uses an electrode that melts and fuses metals together. One of the oldest and simplest welding methods. Works well for thick metals and outdoor applications. Produces slag that needs to be cleaned after welding.
MIG Welding (Metal Inert Gas)
Uses a continuously fed wire electrode and shielding gas (e.g., CO₂, Argon). Ideal for beginners due to easy control. Common in automotive and fabrication industries. Works best indoors, as wind can disrupt the gas shield.
TIG Welding (Tungsten Inert Gas)
Uses a tungsten electrode with a shielding gas (Argon). Produces clean, high-quality welds with excellent precision. Used for thin metals like stainless steel and aluminum. Requires more skill and control than MIG or Stick welding.
Flux-Cored Arc Welding (FCAW)
Similar to MIG welding but uses a tubular wire filled with flux instead of shielding gas. Works well in outdoor environments. Great for welding thicker materials.
Gas Welding
Uses a mixture of oxygen and acetylene to produce a high-temperature flame (up to 3,500°C / 6,332°F). Requires a welding torch, gas cylinders, pressure regulators, and hoses. Used for welding, brazing, cutting, and heating metal. Portable – doesn’t require electricity, making it ideal for remote areas.
Other Methods
- Laser Welding – Used in precision industries like medical devices and electronics.
- Ultrasonic Welding – Common in plastics and electronics.
- Spot Welding – Used in automotive manufacturing.
Tools and Equipment Needed for Welding
Before you start welding, you’ll need the right tools and safety equipment. Here’s a basic list:
- Welding Machine – Choose a MIG, TIG, or Stick welder based on your needs.
- Electrodes/Wire – The type depends on the welding method used.
- Shielding Gas – (For MIG/TIG welding) CO₂, Argon, or a mix of both.
- Protective Gear – Welding helmet, fire-resistant gloves, welding jacket.
Safety Tips for Welding
Just like in Zen, welding requires full awareness – even the smallest mistake can disrupt balance. A master does not dwell on the next move but remains fully present in the action. Concentration is the key to both stability and precision.
Welding involves high heat, electricity, and toxic fumes, so safety is critical. Follow these precautions:
Wear Proper Safety Gear – Always use a welding helmet with auto-darkening features. Work in a Well-Ventilated Area – Welding fumes can be toxic; use an exhaust fan or respirator. Protect Your Skin – UV light from welding can cause burns. Wear long sleeves and flame-resistant clothing. Check Your Equipment – Inspect cables and connections before welding. Avoid Welding Near Flammable Materials – Sparks can ignite nearby objects.
Common Welding Mistakes and How to Avoid Them
Watch this video to learn the 7 most common welding mistakes beginners make:
This video covers issues like improper material preparation and incorrect welding angles.
Conclusion
Welding is an essential skill that opens up many opportunities across various industries. Whether you’re interested in welding for professional work or DIY projects, understanding the basics is the first step.
Want to start welding? Consider practicing on scrap metal and investing in a beginner-friendly MIG welder. Stay safe, keep learning, and soon you’ll be creating strong, high-quality welds!
Did you know ?
A Nuclear Breakthrough in Under 24 Hours!
In 2023, the British company Sheffield Forgemasters achieved something that used to take nearly a year.
They welded a full-sized nuclear reactor pressure vessel in less than 24 hours.How?
Instead of traditional methods, they used LEBW – Local Electron Beam Welding.
A high-energy electron beam, local vacuum, and millimeter-level precision.The result? A super-fast, super-strong weld, ready for the extreme conditions of nuclear infrastructure.
What once took 300 days… now takes just one.
And in nuclear energy, time isn’t just money — it’s safety.